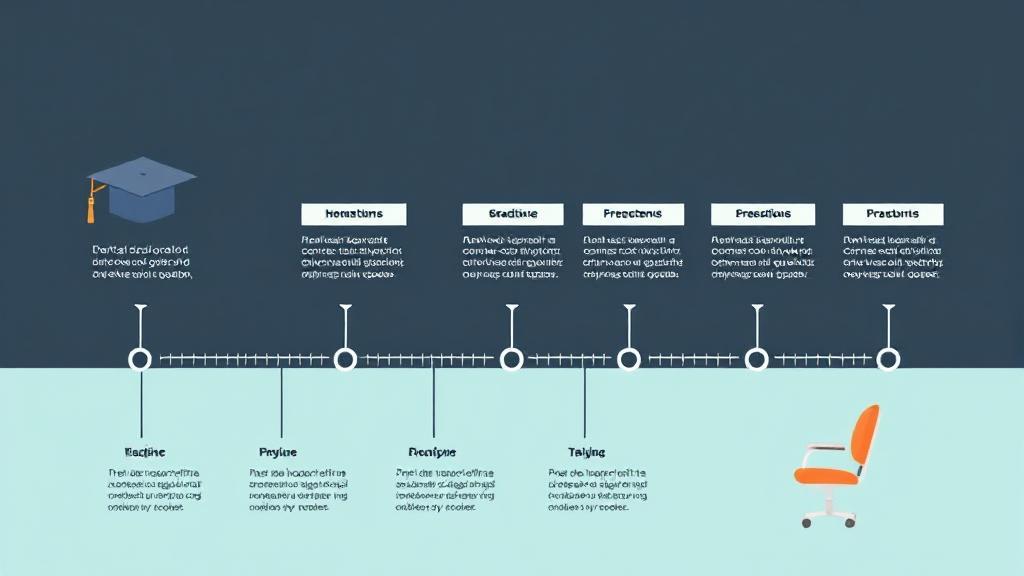
Introduction
Becoming a dentist is a rewarding career choice that requires significant dedication, time, and effort. Dentists play a crucial role in maintaining oral health, diagnosing dental issues, and providing treatment. Understanding the educational path and requirements is essential for those considering this profession.
Pre-Dental Education
High School Preparation
Aspiring dentists should focus on excelling in science and math courses during high school:
- Biology
- Chemistry
- Physics
- Advanced Mathematics
- AP or IB courses when available
Participating in healthcare-related extracurricular activities or volunteering at dental clinics can provide valuable experience.
Undergraduate Degree
A bachelor's degree is mandatory, typically taking 4 years to complete. While no specific major is required, most successful dental school applicants choose:
- Biology
- Chemistry
- Biochemistry
- Pre-dental programs
Prerequisite Courses
Common prerequisite courses include:
- General Biology with lab
- General Chemistry with lab
- Organic Chemistry with lab
- Physics with lab
- Biochemistry
- Anatomy and Physiology
- English
- Mathematics/Statistics
Dental Admission Test (DAT)
The DAT is a standardized test required for dental school admission, typically taken during junior year. The test covers:
- Survey of Natural Sciences
- Perceptual Ability
- Reading Comprehension
- Quantitative Reasoning
Dental School
Duration and Curriculum
Dental school typically lasts four years and is divided into two main phases:
-
Pre-clinical Phase (Years 1-2):
- Classroom and laboratory instruction
- Basic sciences and dental anatomy
- Courses in microbiology, pathology, and dental materials
-
Clinical Phase (Years 3-4):
- Hands-on patient treatment under supervision
- Clinical skills development
- Patient management
- Diagnostic procedures
- Treatment planning
Upon completion, graduates earn either a Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS) or Doctor of Dental Medicine (DMD) degree.
Post-Graduate Training and Specialization
For those pursuing specialization, additional training is required:
| Specialty | Additional Years |
|---|---|
| Orthodontics | 2-3 years |
| Oral Surgery | 4-6 years |
| Pediatric Dentistry | 2-3 years |
| Periodontics | 3 years |
| Endodontics | 2-3 years |
Licensure Requirements
National Board Dental Examination (NBDE)
To practice dentistry, graduates must pass the National Board Dental Examination (NBDE):
- Part I: Covers basic sciences, typically taken after the second year
- Part II: Focuses on clinical dental topics, usually taken in the final year
State Licensing
Requirements vary by state but typically include:
- Completed dental degree
- Passed national boards
- Passed clinical examination
- Background check
- Continuing education commitment
From start to finish, the minimum time required to become a licensed general dentist is approximately 8 years after high school: 4 years of undergraduate education plus 4 years of dental school.
Continuing Education
After becoming licensed, dentists must maintain their credentials through:
- Regular license renewal
- Continuing education credits
- Professional development courses
- Staying current with new techniques and technologies
For more detailed information, visit the American Dental Association or the American Dental Education Association.