Understanding How Nexplanon Works 🔬
What is Nexplanon?
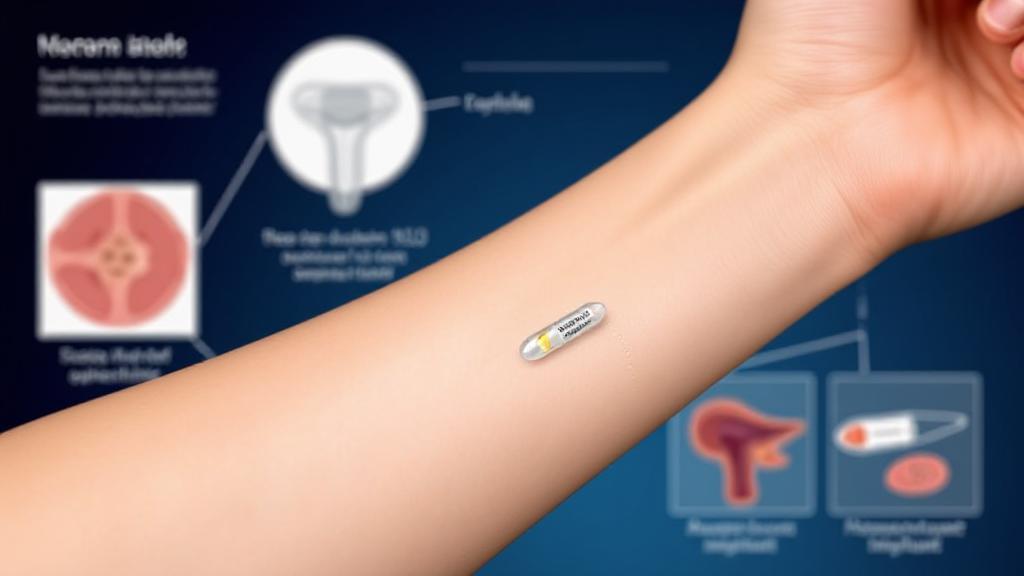
Nexplanon is a type of long-acting reversible contraceptive (LARC) that consists of a small, flexible rod inserted under the skin of the upper arm. This matchstick-sized device releases a synthetic form of progesterone called etonogestrel into the bloodstream, providing continuous birth control for up to three years.
Key Features:
- Duration: Effective for up to 3 years
- Hormone: Contains etonogestrel (progestin)
- Effectiveness: Over 99% effective
- Reversibility: Fertility typically returns quickly after removal
Primary Prevention Mechanisms
1. Ovulation Suppression
The primary way Nexplanon prevents pregnancy is by inhibiting ovulation through:
- Preventing the surge of luteinizing hormone (LH)
- Stopping the release of eggs from the ovaries
- Creating a consistent hormonal environment
2. Cervical Mucus Changes
Nexplanon causes the cervical mucus to become:
- Thicker
- More viscous
- Less penetrable
This creates a hostile environment for sperm, making it difficult for them to travel through the cervix.
3. Endometrial Effects
The hormonal effects of Nexplanon also cause changes to the endometrium (uterine lining), making implantation less likely even if fertilization were to occur.
Timeline of Protection
Benefits of Using Nexplanon
- Long-term protection
- Low maintenance
- Discreet
- Quick fertility return after removal
- Highly effective contraception
Potential Side Effects
Common effects may include:
- Changes in menstrual bleeding patterns
- Headaches
- Weight gain
- Mood changes
- Acne
For a more detailed list of side effects, visit the Mayo Clinic's page on Nexplanon.
Healthcare Provider Role
The implant must be inserted and removed by a trained healthcare provider. The procedure is:
- Quick (usually less than 5 minutes)
- Done under local anesthetic
- Performed in an outpatient setting
Monitoring and Follow-up
While Nexplanon doesn't require regular maintenance, it's important to:
- Check the insertion site periodically
- Be aware of the expiration date
- Schedule removal or replacement after 3 years
- Contact your healthcare provider if you experience concerning side effects
For more information about contraceptive options, visit the Planned Parenthood website or the FDA's official page on birth control methods.