Understanding the Building Blocks of Life 🧬
A cell is the fundamental unit of life - the smallest structure capable of performing all the processes that define living organisms. Whether examining a single-celled bacterium or a complex multicellular organism like a human, cells are essential to all living things.
The Discovery and Theory of Cells 🔬
The concept of cells emerged in the 17th century when Robert Hooke observed cork through a microscope and coined the term "cell." Later, Anton van Leeuwenhoek advanced cell study by observing living "animalcules" through improved microscopes.
The cell theory, developed by scientists Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolf Virchow, established three fundamental principles:
- All living organisms are composed of one or more cells
- The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things
- All cells arise from pre-existing cells
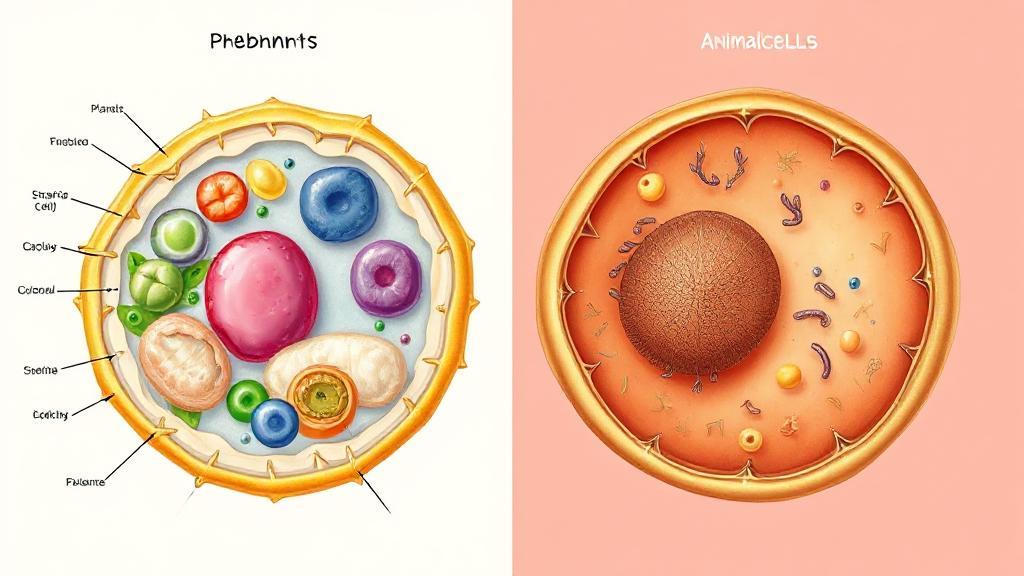
Types of Cells
Prokaryotic Cells
- Lack a nucleus
- Simpler structure
- Smaller in size
- DNA located in nucleoid region
- Examples: Bacteria and Archaea
Eukaryotic Cells
- Contain a nucleus
- More complex structure
- Larger in size
- Possess membrane-bound organelles
- Examples: Plants, animals, fungi, and protists
Cell Structure and Components 🏗️
Additional important organelles include:
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): Protein and lipid synthesis network
- Golgi Apparatus: Modifies and packages proteins and lipids
- Lysosomes: Contain digestive enzymes
- Chloroplasts (in plant cells): Sites of photosynthesis
Most cells are microscopic, ranging from 1-100 micrometers in diameter. However, some specialized cells, like nerve cells, can extend up to a meter in length!
Cell Functions 🏃♂️
Cells perform numerous vital functions:
- Energy production
- Protein synthesis
- Waste elimination
- Growth and reproduction
- Response to environmental stimuli
- Metabolism
- Development of tissues and organs
Cell Communication and Specialization 📱
Cells communicate through:
- Chemical signals
- Electrical impulses
- Physical contact
In multicellular organisms, cells differentiate for specific functions:
- Nerve Cells: Signal transmission
- Muscle Cells: Movement
- Red Blood Cells: Oxygen transport
Importance in Biology 🌍
Understanding cell biology is crucial for advances in medicine, genetics, and biotechnology. From studying diseases to developing new therapies, cell research continues to drive scientific discovery.
For more detailed information, explore these resources:
- National Center for Biotechnology Information
- American Society for Cell Biology
- Cell Biology by the Numbers
Remember: Every living thing you see is made up of these microscopic marvels, working together in perfect harmony to sustain life! 🌟